ATP SYNTHASE STRUCTURE
Education
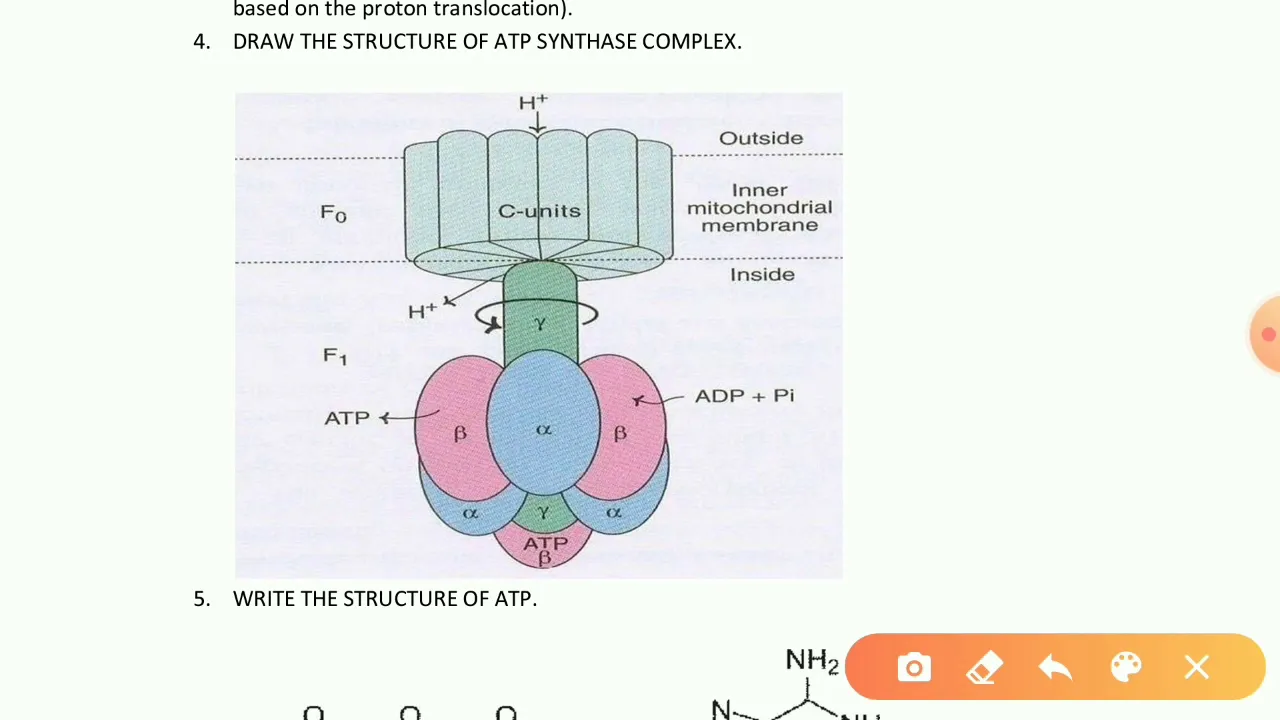
Introduction
ATP synthase, also known as Complex V, is a crucial enzyme found in the oxidative phosphorylation process in cells. It is a remarkable molecular machine composed of multiple subunits working together to produce ATP, the main energy currency for cells. This enzyme consists of various subunits, including the Gamma subunit essential for regulating ATP production, and the Alpha and Beta subunits responsible for organizing the Gamma subunits. The arrangement of these subunits plays a significant role in the functioning of ATP synthase, ensuring efficient energy production for cellular activities. By converting a proton gradient into ATP, ATP synthase plays a vital role in cellular energy metabolism.
Keywords
ATP synthase, oxidative phosphorylation, subunits, Gamma subunit, Alpha and Beta subunits, energy production, cellular metabolism
FAQ
What is the role of ATP synthase in cells? ATP synthase is responsible for producing ATP, the primary energy source for cellular activities, by converting a proton gradient into ATP molecules.
What are the key subunits of ATP synthase? The ATP synthase enzyme consists of various subunits, including the Gamma subunit, which regulates ATP production, and the Alpha and Beta subunits, which organize the Gamma subunits for efficient energy production.
How does the structure of ATP synthase contribute to its function? The arrangement of subunits within ATP synthase is crucial for its functioning, ensuring the efficient conversion of proton gradients into ATP molecules for cellular energy metabolism.

